5 Common Thyroid Diseases in Women
One tiny gland can change your life.
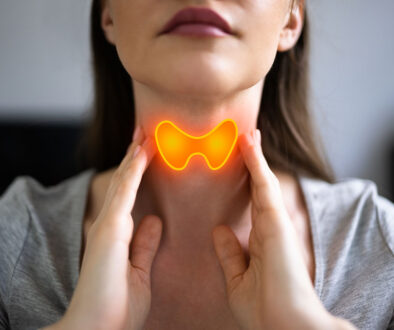
The thyroid is a small, butterfly-shaped gland only about two inches long that is located in the throat at the base of the neck. It processes iodine from your diet into thyroid hormone.
But don’t be fooled by the size; this little gland has a big impact on your overall health, and as internal medicine specialists in Cary, we’re in the perfect position to help those with thyroid problems.
.
When something goes wrong with your thyroid, it can transform your life. While thyroid problems aren’t limited to women, they are more commonly found in women than men.
According to the American Thyroid Association:
- Roughly 20 million Americans have some kind of thyroid disease, but only 40 percent are aware that they have one.
- Women are almost eight times more likely to have a thyroid problem than men. In fact, 1-in-8 women will develop thyroid disease in her life.
- Thyroid issues can put you at risk for certain other diseases.
We’ll examine what the thyroid does, the most common types of thyroid disease, and how these disorders affect your everyday life.
What Does the Thyroid Do?
The thyroid gland is an important part of the endocrine system, which provides instructions to the body’s cells. Its main purpose is to regulate and control your metabolism, particularly by producing hormones T4 and T3. These hormones are vital because they tell your cells how much energy to use.
Ideally, your thyroid consistently makes the right amount of these hormones, releasing them and creating new ones when the T4 and T3 hormones in your system have been used. These thyroid hormones are reserved or released by the pituitary gland, which serves as a type of “gatekeeper” by controlling the amount of hormones that enter the bloodstream.
The pituitary gland also evaluates your body to see if there is too much or too little of these thyroid hormones and as a result, it adjusts its own hormone, which is called a thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH). The TSH is then sent to the thyroid with the goal of balancing the amounts to make sure there isn’t too much or too little in the bloodstream.
Together, the thyroid and pituitary gland work to help ensure that your body’s systems are in perfect sync.
When these thyroid hormones are too high or too low, it can pave the way for problems that affect your entire body.
Thyroid disease is very common, particularly among women and those middle-aged or older, and the most common are hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism, Hashimoto’s disease, Graves’ disease and goiters.
HYPERTHYROIDISM
Hyperthyroidism occurs when the thyroid produces more hormone than the body needs; this is also called thyrotoxicosis.
As a result, many body functions speed up, increasing your metabolism and causing other issues such as a faster heartbeat and nervousness.
Roughly one percent of the U.S. population has hyperthyroidism.
Its symptoms may include:
- Fatigue
- Insomnia or trouble sleeping
- Hand tremors
- Mood swings
- Irregular and rapid heartbeat
- Diarrhea
HYPOTHYROIDISM
Hypothyroidism occurs when the thyroid does not make enough thyroid hormone, and as a result, body functions may slow down.
According to the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism, an estimated 4.6 percent of the U.S. population over age 12 has hypothyroidism.
Women are more likely to develop hypothyroidism than men, but because it develops slowly over a period of time, many do not immediately notice symptoms of the disease. However, when symptoms appear, they include:
- Joint and muscle pain
- Constipation
- Dry skin
- Fatigue
- Dry, thinning hair
- Depression
- Irregular menstrual periods
- Slowed heart rate
HASHIMOTO’S DISEASE
This disease is one of the main causes of hypothyroidism.
In Hashimoto’s disease—also referred to as chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis– your thyroid is attacked by your immune system, which means that Hashimoto’s disease is an autoimmune disorder.
Hashimoto’s disease can occur in any one of any age, but it primarily impacts women in middle age, and our doctors can conduct a simple test to determine if you have it.
Those more likely to develop Hashimoto’s include:
- Those who have been exposed to excessive radiation
- Those with other autoimmune diseases such as lupus or rheumatoid arthritis
- Those who have family members with thyroid problems or autoimmune diseases
GRAVES’ DISEASE
Graves’ disease can lead to hyperthyroidism, and like Hashimoto’s disease, it is also an autoimmune disorder. It’s most often seen in those under 40 and among women.
One of the most distinguishing features of Graves’ disease is that the disorder causes bulging eyes, a condition known as Graves’ ophthalmopathy. Another hallmark sign is thick red skin on the top of the feet or shins; this is known as Graves’ dermopathy.
Other symptoms include:
- Sleep problems
- Anxiety
- Issues with libido or even erectile dysfunction
- Changes in menstrual cycles
- Heat sensitivity
- Unintentional weight loss
GOITERS
A goiter is an enlarged thyroid that can be caused by lack of iodine in the diet. Not only can it cause the neck to look swollen, but it can also interfere with swallowing and breathing.
However, in the United States salt is typically iodized, and therefore, goiters are more likely due to hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism.
ARE YOU AT RISK FOR DEVELOPING A THYROID DISORDER?
Those more likely to develop thyroid disorders are those who:
- Have had a goiter or previous thyroid surgery
- Have had autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis or type 1 diabetes
- Are over age 60
- Have had a baby within the last six months
- Have a family history of thyroid disease
Treatment for Thyroid Disorders at Cary Medical Group
As internal medicine doctors in Cary, we have treated many patients who have faced the challenge of thyroid problems, and often, treatment is simple, effective and straightforward.
How Is Thyroid Disease Treated?
Treatment depends upon the type of disorder you have.
Disorders that cause hypothyroidism are usually resolved by taking a thyroid hormone medication orally to successfully restore your hormone levels to where they should be.
Likewise, hyperthyroidism can be treated by using oral medication.
However, we recognize that every patient is different, and that’s why we tailor our approach to be appropriate for you. Only your physician at Cary Medical Group can prescribe the course of treatment that is right for you.
Cary Medical Group: More Than Four Decades of Serving the Community
We have a vested interest in the Cary area. After all, you’re not just a patient—you’re a member of the community in which we all live.
For more than 25 years, we have served as the internal medicine practice of choice for Cary residents. Looking for a new medical home? We would love to meet you and work with you to create the healthiest life possible.
Schedule an appointment today.